
People often have no doubt that they have human papillomavirus (HPV) in their bodies. This is because the papillomavirus is usually in a latent form suppressed by natural immunity. Problems arise when they get out of control and begin to actively manifest themselves in the form of growths in various parts of the body. Men suffer less from the effects of the virus than women, but for them the effects can turn into serious problems in the form of papillomas in the penis.
Causes
Viral DNA enters the body through micro-cracks in the skin or mucous membranes. If a man's immunity weakens, the first signs of HPV will appear a few months after infection.
Up to 80% of transmission is sexual. Barrier contraception minimizes the risk of infection, but does not completely eliminate it.
Other ways of infection:
- Home road.The virus is transmitted along with an infected person's personal belongings: clothing, hygiene products, etc. If the skin is damaged, even small, the risk of infection increases. This pathway is characterized by infection with low oncogenic virus species. They do not cause serious health problems, but appear in the form of genital warts, papillomas and warts, creating a cosmetic defect.
- From mother to child.If a mother becomes infected with HPV during pregnancy and childbirth and gives birth naturally, the baby is more likely to be infected.
If a man has good immune defenses, the virus does not manifest itself and can remain hidden in the body for a long time. Therefore, the danger is not the virus itself, but the weakening of the immune system, which leads to the activation of HPV.
There are a number of factors that affect the likelihood of a virus strengthening its position:
- chronic diseases;
- hormonal problems;
- incorrectly chosen contraception or its complete absence;
- viral infections;
- alcohol, smoking or long-term antibiotic use;
- frequent stress.
All these factors negatively affect the immune system. If there is more than one trigger in a person's life, it will lead to faster development of the papillomavirus.
symptoms
Often papillomas appear only from the outside, but in some casesNon-specific symptoms may occur:
- itching and burning during sexual intercourse;
- pain when touching papillomas;
- accumulation of urine in penile wrinkles;
- Unpleasant odor in the affected area.
In addition, neoplasms can grow and affect not only the penis area, but also the anus and pubis.
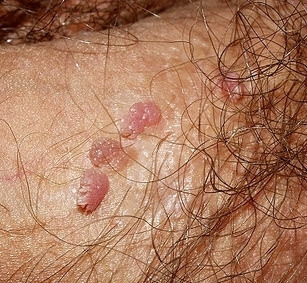
What do papillomas look like?
Penile papilloma is a small neoplasm. At first, it may appear alone, but without proper treatment, the number of papillomas increases. However, they can unite with each other.
These growths are similar to fleshy or pink cauliflower blooms. They are often localized in the foreskin, head and frenum. Less commonly, it is diagnosed in the urethra and scrotum. Papillomas can also look like small white pimples that appear in long rows. This form is typical for localization in the bridle area.
One of the manifestations of HPV is Buschke-Levenstein warts. It is distinguished by its rapid growth, remarkable size and resistance to various treatments. The appearance is associated with several existing papillomas and warts that join together and form a large lesion area. Buschke-Levenstein condyloma is dangerous because the cells it changes can easily turn into cancer.
Which doctor should you contact
As a rule, urologists diagnose papilloma in men. If you have genital warts in the anal area, you can also consult a dermatovenerologist or proctologist. However, papillomas are usually referred to a surgeon for removal. In general, the diagnosis occurs in several stages:
- The urologist examines the patient and conducts interviews.Oral questioning should be performed to assess the patient's lifestyle and determine the cause of the viral infection. Visual examination includes not only the condition of the penis, but also the assessment of adjacent organs - the scrotum, anal area. This is necessary to complete the localization pattern of the virus.
- Urethral smear.Determines the presence of various sexually transmitted diseases.
- PCR.This test not only shows the presence of HPV in the body, but also most likely determines its type.
- Meatoscopy.This procedure is an examination of the urethra if the papillomavirus is infected with phrenum. After the
- papilloma has been removed, the doctor may order a biopsyto assess the condition of the removed tumor. This is to eliminate the risk of developing cancer and to ensure that the papilloma is benign.
In this case, it is desirable to conduct a survey between both partners. Generally, a woman is infected with one of the types of papillomavirus. If only one man is treated, he is more likely to get sick again after a while.
Why are papillomas dangerous?
Human papillomavirus is often associated with other related diseases. The appearance of papillomas in the area of the glans penis helps to accumulate urine in wrinkles. This creates the conditions for the emergence and growth of various microorganisms, resulting in infections. They can cause erosion around the papilloma and can also contribute to inflammation of the urethra and testicles. These diseases are characterized by problems with urination, pain and high fever.
Another danger is the trauma of neoplasms that cause bleeding. This is due to the formation of many blood vessels around the papillomas that supply blood. Minor damage can also cause infection due to injury.
Neoplasms can also rub while moving, which can cause pain and discomfort.
HPV and cancer
When the virus begins to spread, neoplasms become sporadic and benign. They grow without treatment and unite with each other. Over time, cells degenerate into malignant cells.The risk of cancer is especially high if a man is infected with a highly oncogenic type of virus - 16 or 18.These are the causes of penile and bladder cancer.
Treatment of papillomas
HPV treatment involves not only eliminating the external manifestations, but also strengthening the immune system, which is necessary to prevent the manifestations of the virus.Immunostimulating drugs are used to maintain immunity.
As an antiviral drug, an ointment that suppresses the growth of the virus and eliminates small growths is effective. It does not always end with the task of removing it completely, but it prevents the appearance of new growths. Antiviral ointment is prescribed to stimulate immunity. The ointment does not clear papillomas, but helps to activate the cells of the immune system, which stops their growth and development.
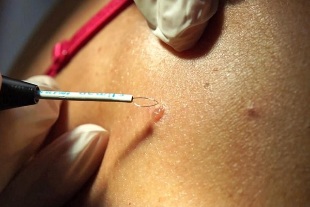
Lifting methods
There are several ways to get rid of new growths:
- Laser removal.The laser beam affects the papilloma, which completely burns the growth. After a few weeks, a crust forms here. The method is considered effective due to the absence of relapses. Removal is performed under anesthesia. No bleeding, no scars.
- Cryodestruction.Papillomas are exposed to liquid nitrogen. It immediately freezes the desired area, the neoplasm on it collapses and dies. The disadvantage of this method is the inability to control the depth of cryodestruction. In the place of the removed papilloma, a crust remains and disappears after a while.
- Radiosurgery.The principle of this method is similar to laser cleaning. Radio waves do not leave scars and are pre-anesthetized with a special spray before the procedure. After that, there are no complications and the body recovers quickly.
- Electrocoagulation.Growth is affected by an electric current, so the leg is removed and then the papilloma disappears. Superficial anesthesia may be given if necessary. The procedure takes a few minutes, is extensive and affordable. However, this method is able to leave scars after healing.
- Surgical intervention.Rarely used when the tumor is very large. It is performed under anesthesia, heals and trauma for a long time. The method is good in that it allows to preserve the growth removed for histological examination.
The cost of each method depends on the complexity of the case, the size and number of papillomas to be removed.
Consult your doctor before choosing a method. It will explain to you what is best to use in your situation, explain in detail how the procedure is performed. It is also advisable to obtain material for histology after removal of the neoplasm. This is necessary to determine whether benign neoplasms have begun to degenerate into malignant ones. This method will help detect early cell changes and prevent the spread of cancer.














































































